Archive
Topics
The Archive module allows you to create compressed data files (zstd) from Data Node indices. The archive checks the age of each document in the index and if it is older than defined in the job, it is copied to the archive file.
Configuration
Enabling module
To configure the module edit the UI main configuration file end set path to the archive directory - location where the archive files will be stored:
vim /etc/logserver-gui/logserver-gui.yml
remove the comment from the following line and set the correct path to the archive directory:
archive.archivefolderpath: '/var/lib/logserver_archive_test'
Archives will be saved inside above directory in the subdirectories that describes year and month of its creation. For example:
/var/lib/logserver_archive_test
├── 2022
│ └── 08
│ ├── enc3_2022-08-15.json.zstd
│ └── skimmer-2022.08_2022-08-06.json.zstd
└── 2023
├── 05
│ ├── enc1_2023-05-25.json.zstd
│ ├── enc2_2023-05-25.json.zstd
│ └── skimmer-2023.05_2023-05-25.json.zstd
└── 07
└── skimmer-2023.07_2023-07-30.json.zstd
Archive Task
Create Archive task
From the main navigation go to the “Archive” module.
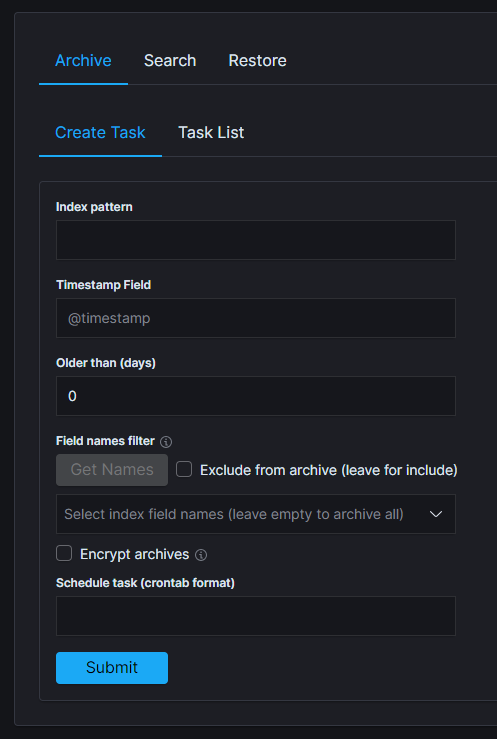
On the “Archive” tab select “Create Task” and define the following parameters:
Index pattern- for the indices that will be archived, for example,syslog*Timestamp Field- time field of the indices (default @timestamp)Older than (days)- number of days after which documents will be archivedField names filter- filter fields that should be archivedEncrypt archives- after enabling encryption, prompt with two password fields will be shown.Schedule task(crontab format) - the work schedule of the ordered task.
Task List
In the Task List, you can follow the current status of ordered tasks. You can modify the task scheduler or delete a single or many tasks at once.
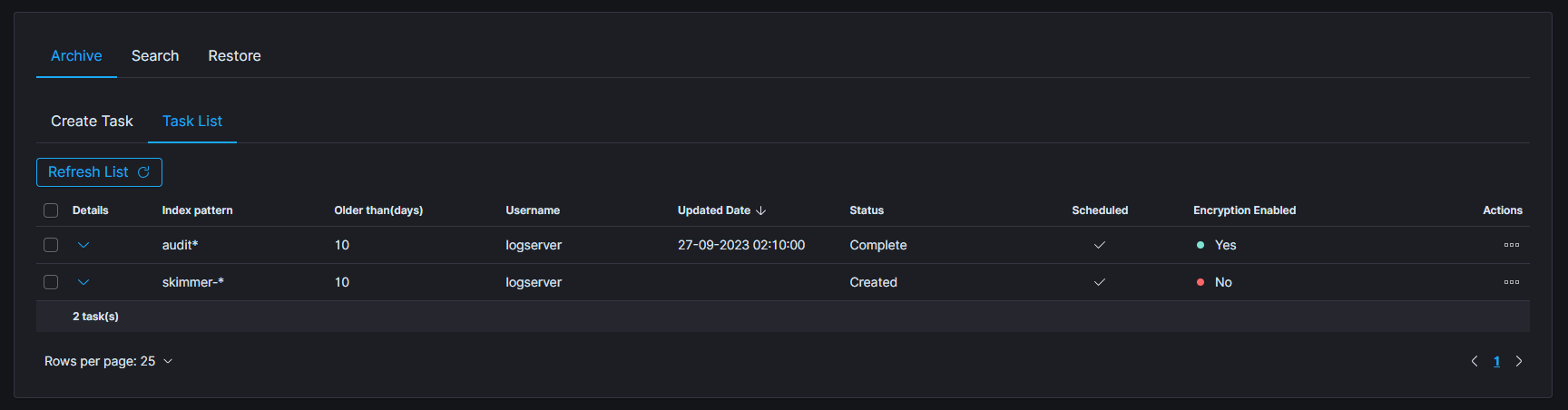
If the archiving task finds an existing archive file that matches the data being archived, it will check the number of documents in the archive and the number of documents in the index. If there is a difference in the number of documents then new documents will be added to the archive file.
To show more details of the task, click on the details cell of the desired row.
Archive Search
The Archive Search module can search archive files for the specific content and back results in the Task List
Create Search task
From the main navigation go to the
Archivemodule.On the
Searchtab selectCreate Taskand define the following parameters:Select range of listed archives- files that matches selected range will be displayed in the list (default last 14 days)Search text- field for entering the text to be searchedFile name- list of archive files that will be searchedEnable searching in encrypted archives- enable option to search in encrypted archives.
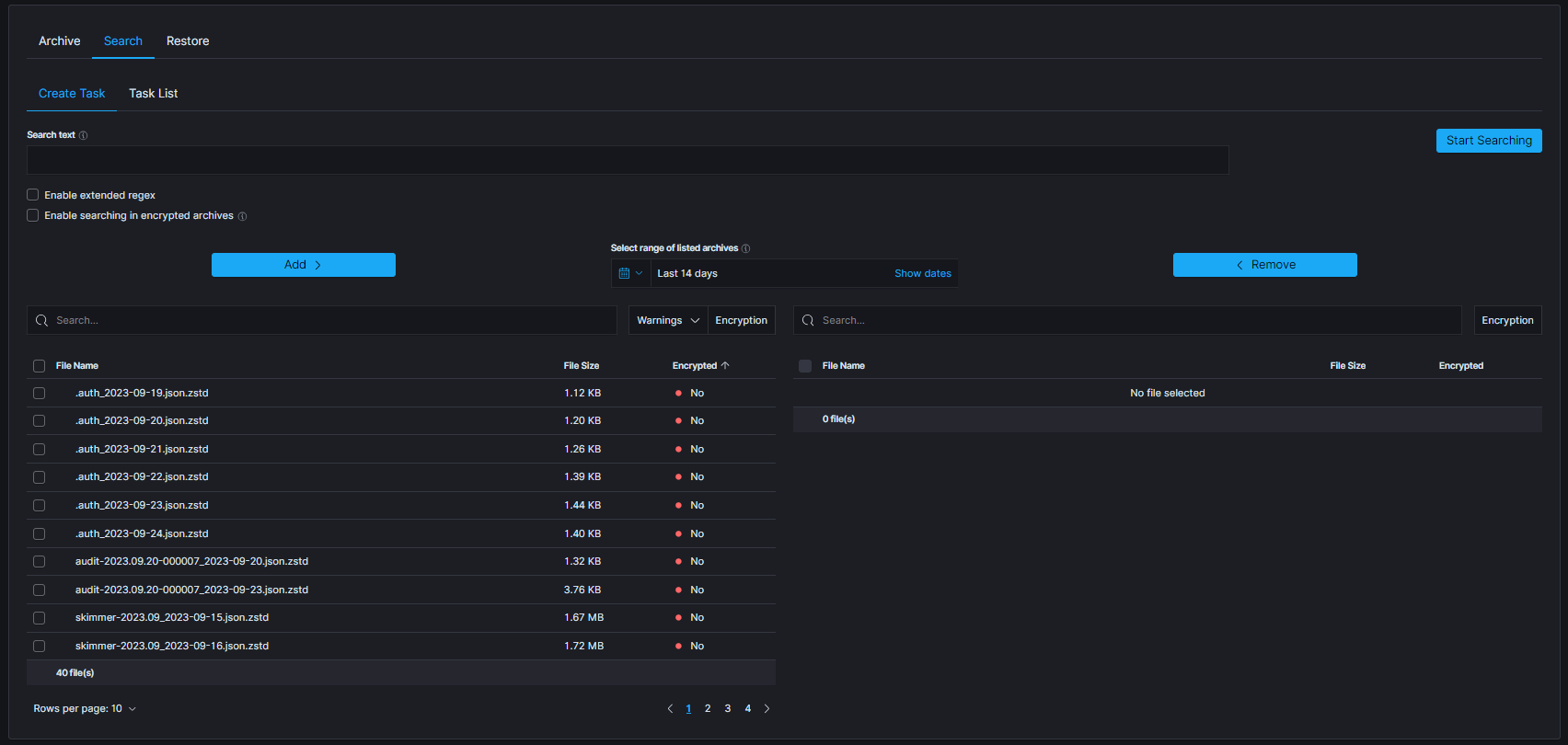
The table footer shows the total number of found files for the specified date range.
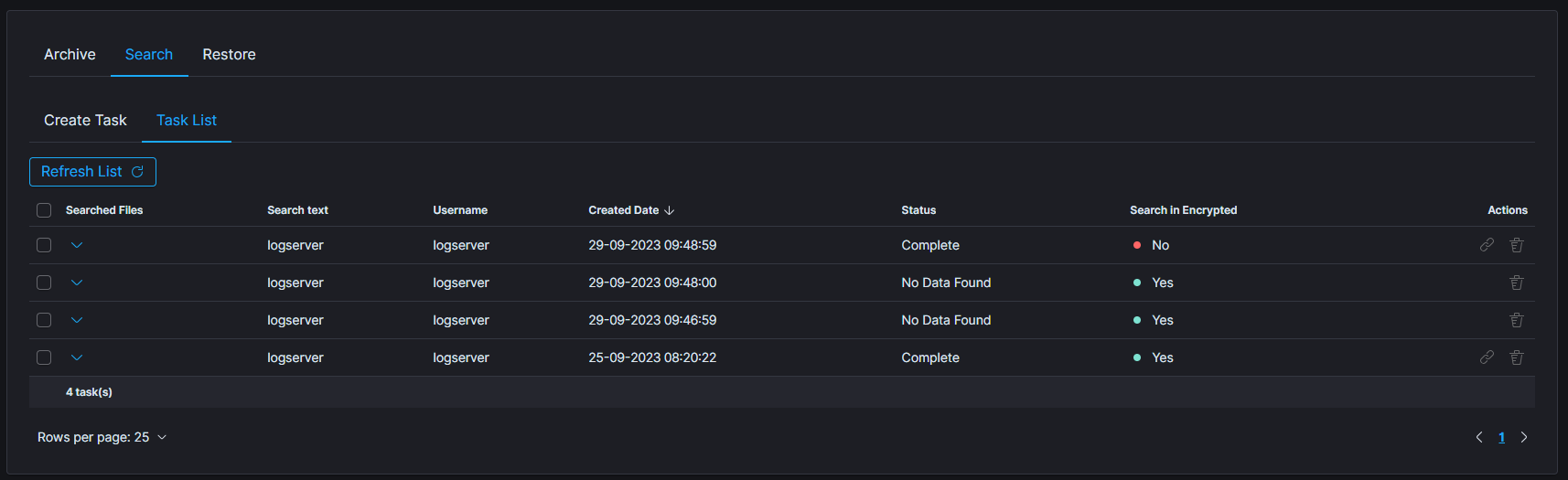
Task list
The searching process can take a long time. On the Task List, you can follow the status of the searching process. Also, you can view results and delete tasks.
Archive Restore
The Archive Restore module moves data from the archive to the Data Node index and make it online.
Create Restore task
From the main navigation go to the
Archivemodule.On the
Restoretab selectCreate Taskand define the following parameters:
Select range of listed archives- files that matches selected range will be displayed in the list (default last 14 days)Destination index- If a destination index does not exist it will be created. If exists data will be appendedFile name- list of archive files that will be recovered to the Data Node indexEnable restoring from encrypted archives- enable option to restore data from encrypted archives
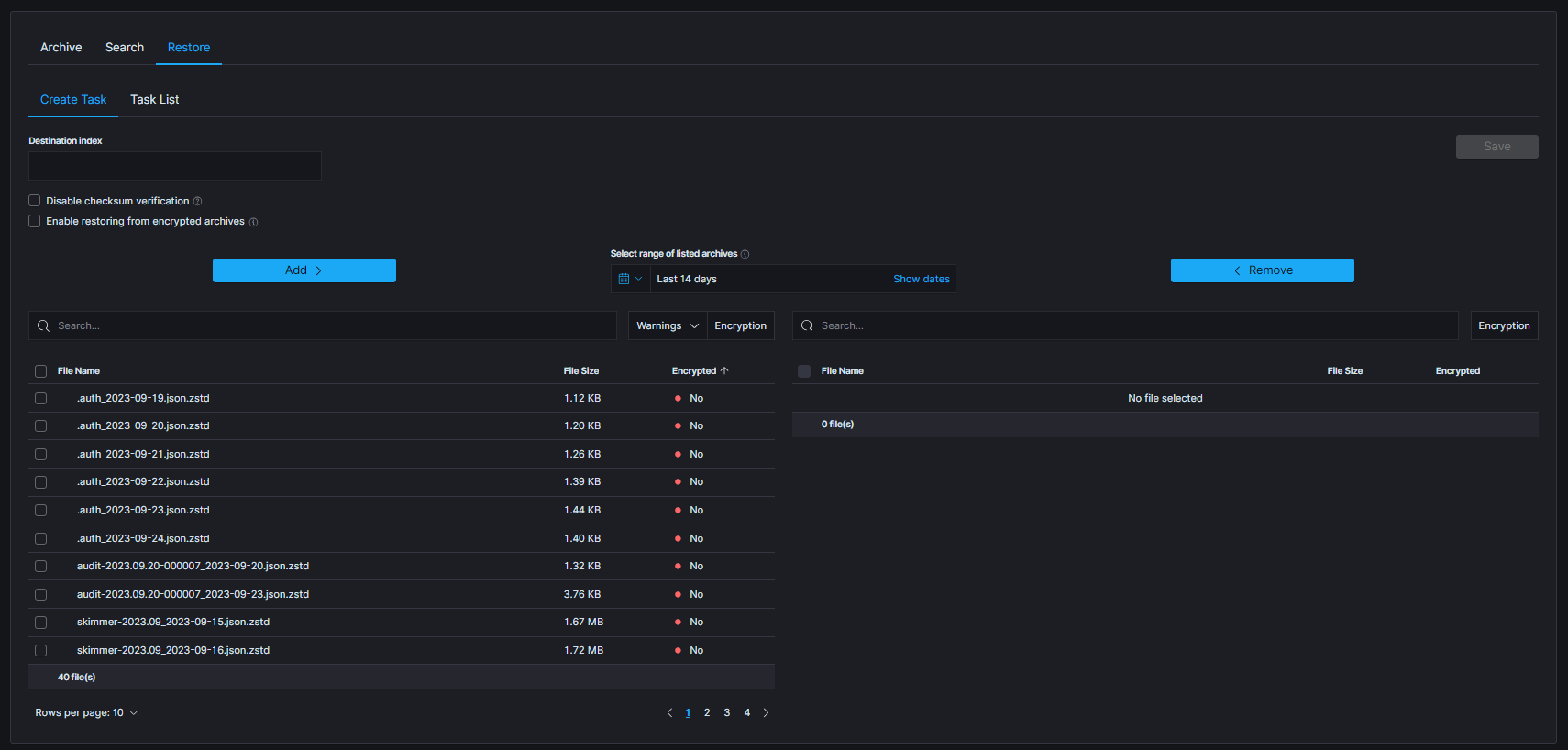
The table footer shows the total number of found files for the specified date range.
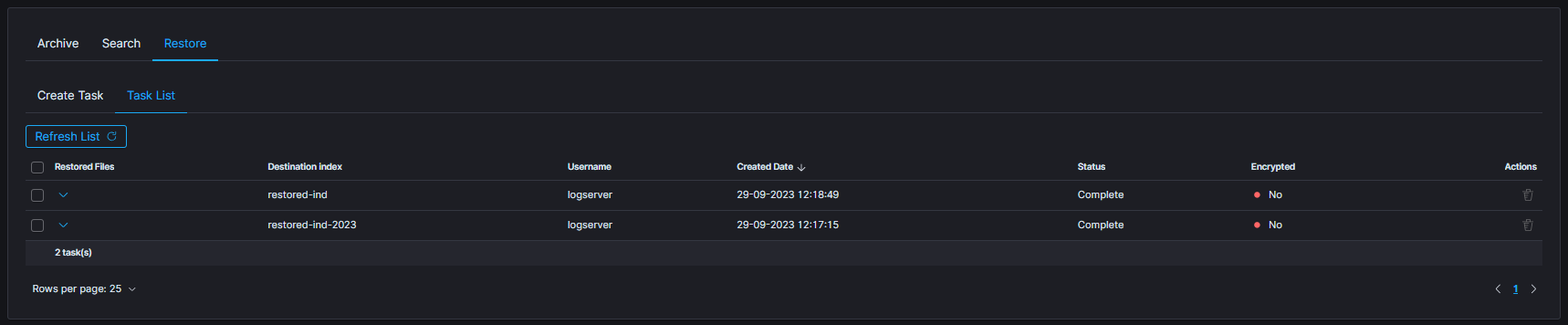
Task List
The process will index data back into the Data Node. Depend on archive size the process can take long time. On the Task List you can follow the status of the recovery process. Also you can view result and delete tasks.
Search/Restore task with archives without metadata
When creating Search or Restore tasks, during selection of archives to use, some warnings could be seen. Following screenshot presents list of archives with enabled filter that shows only archives with warnings:
missing metadatamissing archive file
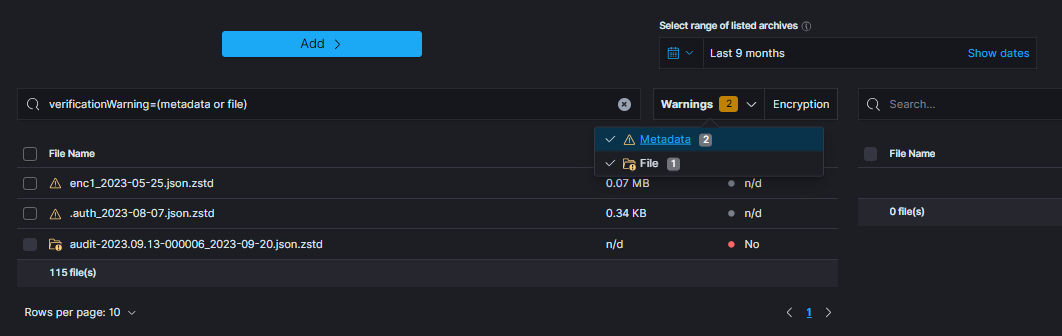
When particular archive’s metadata could not be found following icon will be displayed:
![]()
That archive can be used for task creation, but there are some issues to keep in mind:
encryption status of the archive without metadata cannot be established (can be either encrypted or not)
when task has enabled encryption handling (e.g.
Enable restoring from encrypted archivesorEnable searching in encrypted archives), archives will be decrypted with provided password. If archive was not decrypted, an error is expectedwhen archive is potentially encrypted and password is not provided, an error is expected.
On the other hand, when metadata is present, but archive itself could not be located, following icon will be displayed: ![]()
That archive cannot be used for task creation and so cannot be selected.
Archive Clean
The Clean tab allows you to delete data from the archive.
To do so, go to the Clean section in the Archive tab.
Then, check the boxes next to the files you want to delete and press the Delete button in the top right corner.
Archive Directory Structure
New archives will be created in the configured archive.archivefolderpath in a systematic order. They can be found under a path based on the date the archive was created: /\(archivefolderpath/\)year/$month. This method of storing archives ensures better readability and significantly simplifies viewing large numbers of files. The final directory is determined by the last segment of the archive name, which contains the archive creation date. For example, assuming that the root archivefolderpath is set to /download, archive sample-archive_2023-11-01.json.zstd will be saved to the /download/2023/11/ automatically created directory. Archives once saved to the root directory will be displayed normally in the GUI and will be accessible in the same way as those saved in a sorted manner.
Archives Checksum Verification
Archives checksum verification feature has been integrated into the Create Task section, enhancing the functionality of both the Search and Restore tabs. This feature adds an extra layer of confidence in the accuracy and reliability of the stored files.
Starting Verification
To start the verification process navigate to one of the mentioned tabs. Select archives that will be checked and move them to the right-side table. Below picture presents the button that will be activated, as soon as any complete archives (without any warning) will be selected in the right table. Archives without metadata cannot be utilized due to the lack of necessary details.
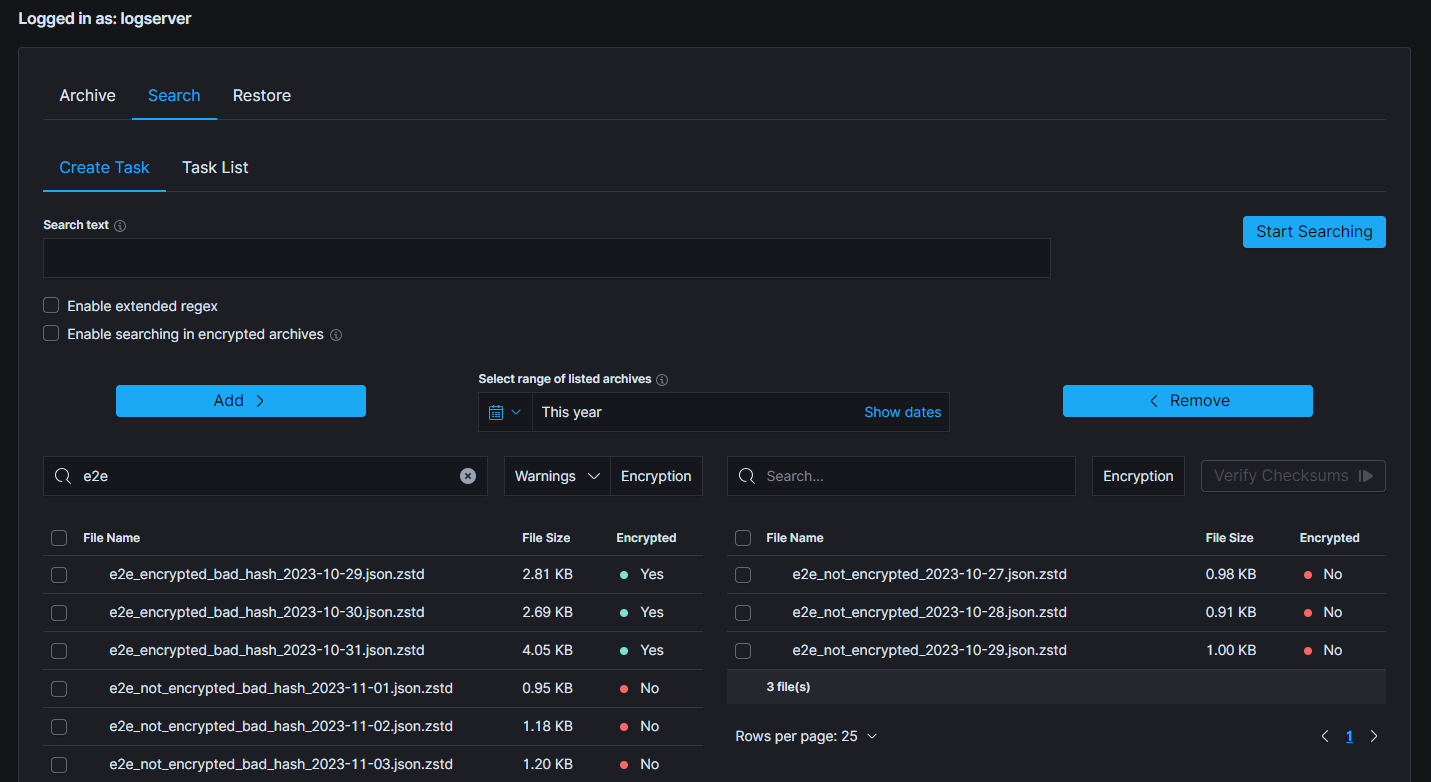
In order to optimize resource utilization and enhance the overall efficiency, a double selection mechanism has been implemented for the file checksum verification, acknowledging the resource-intensive nature of this feature. This ensures, that only desired files will be processed.
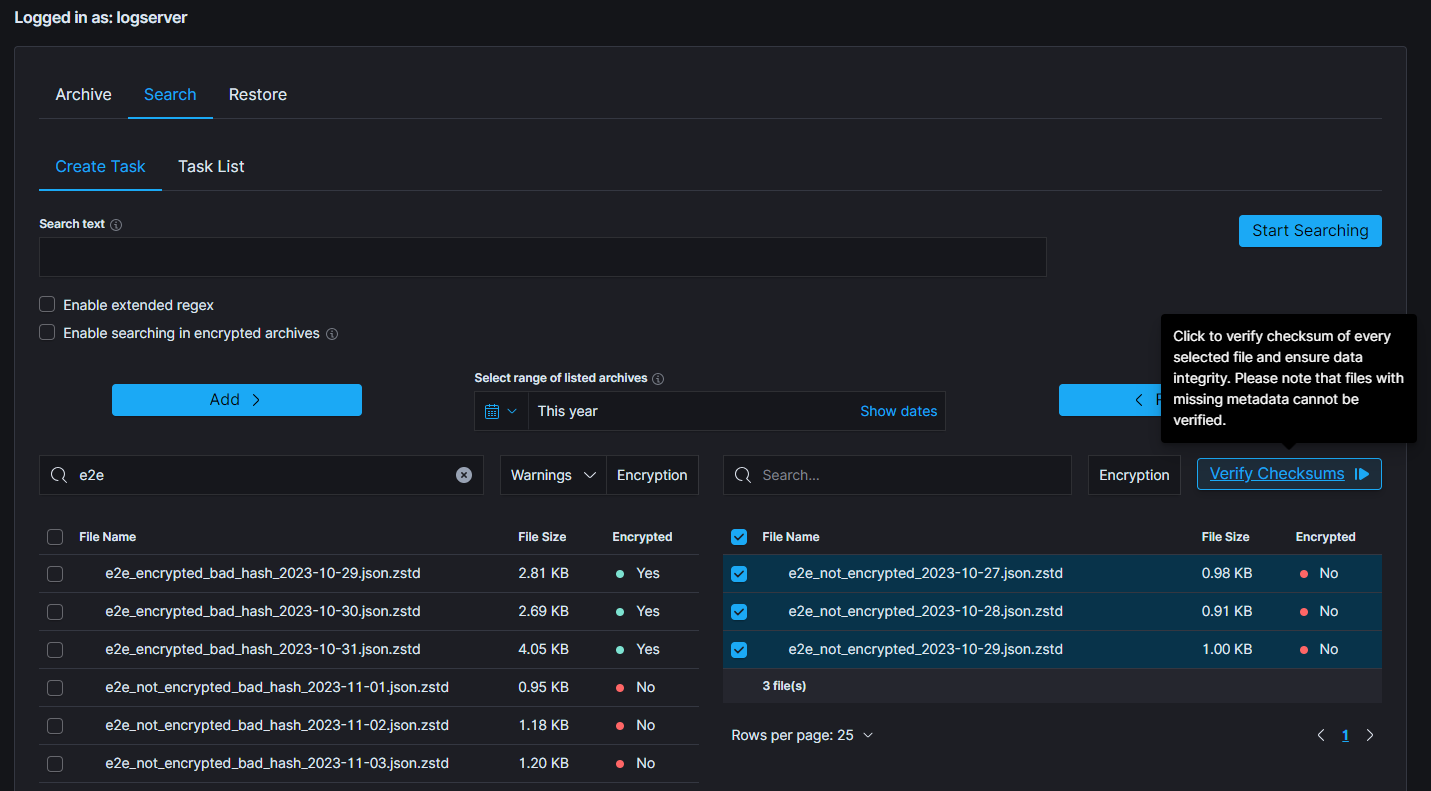
Above picture presents correctly selected archives and a situation when verification process can be started by clicking the Verify Checksums button. Following modal will be displayed.
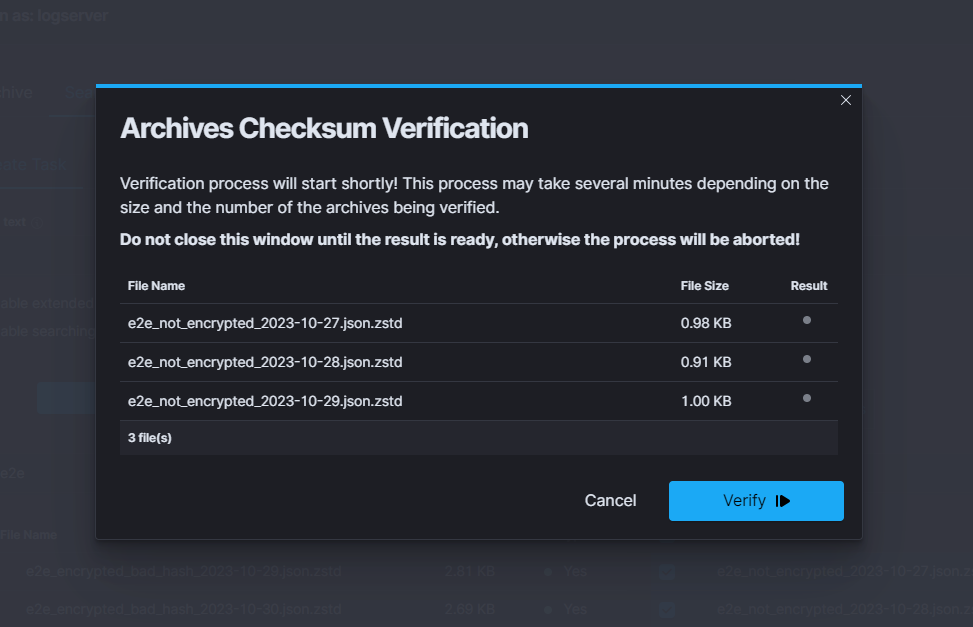
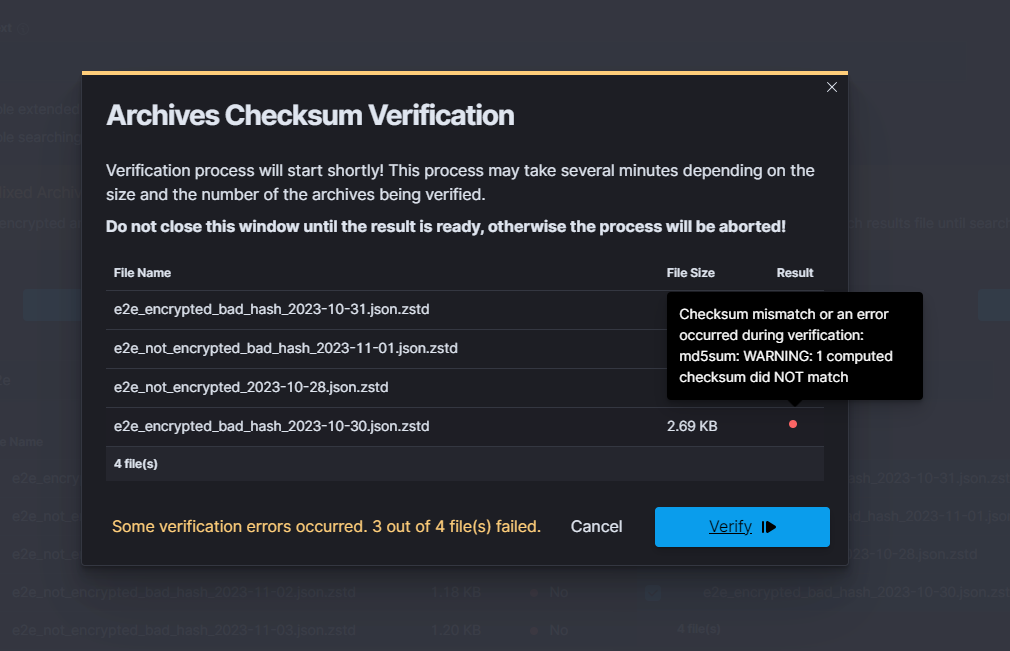
Showcased modal displays previously selected files and some of its details, such as its size and result of verification. Hovering over the result dot provide users with additional information about the result, eg. current status of the verification or possible error.
To start verification, simply click the Verify button in the bottom right corner.
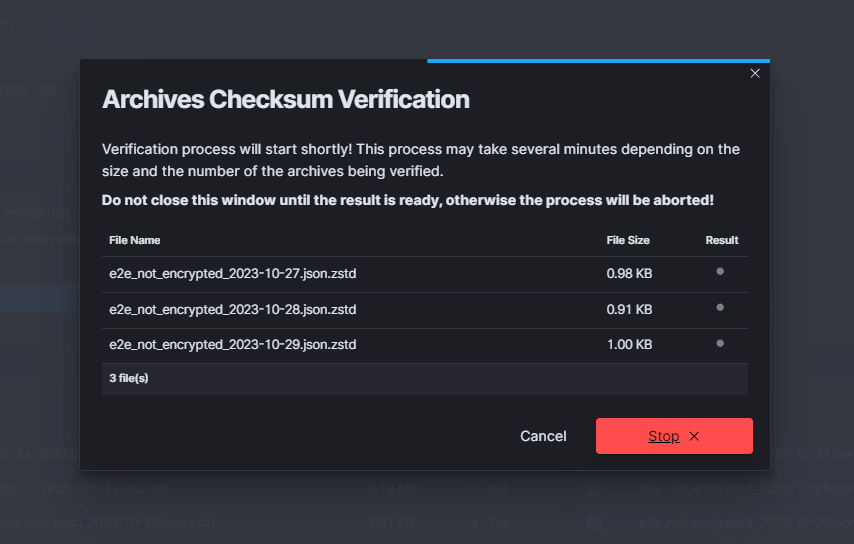
After verification has been started, the loading progress bar will be displayed, indicating that the process is running. It is worth mentioning that neither this modal nor the page should be closed or reloaded as the verification process will stop immediately.
The verification can be either stopped or cancelled, by clicking one of the two buttons.
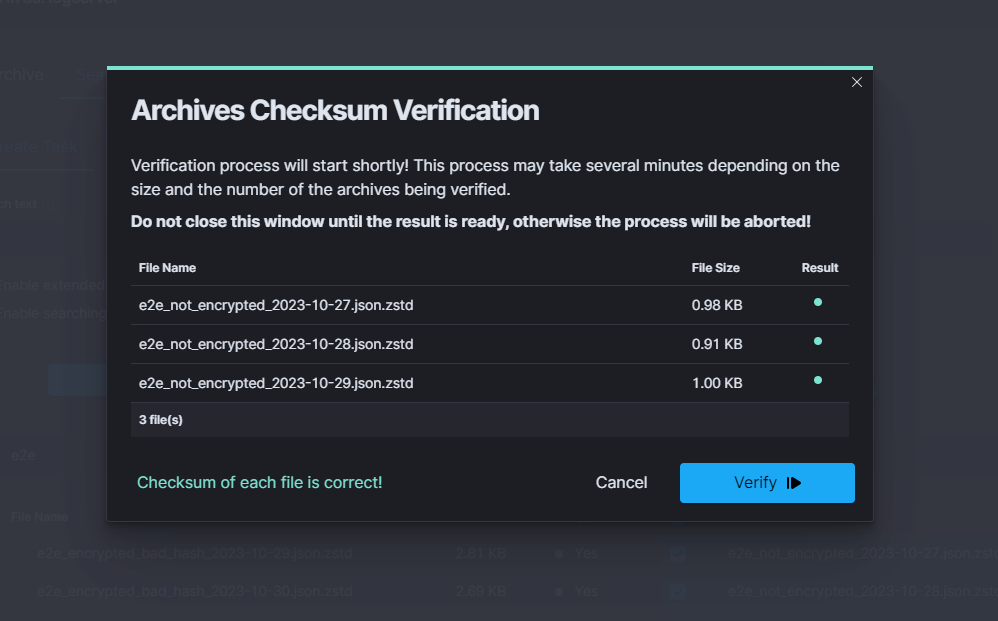
Verification Result
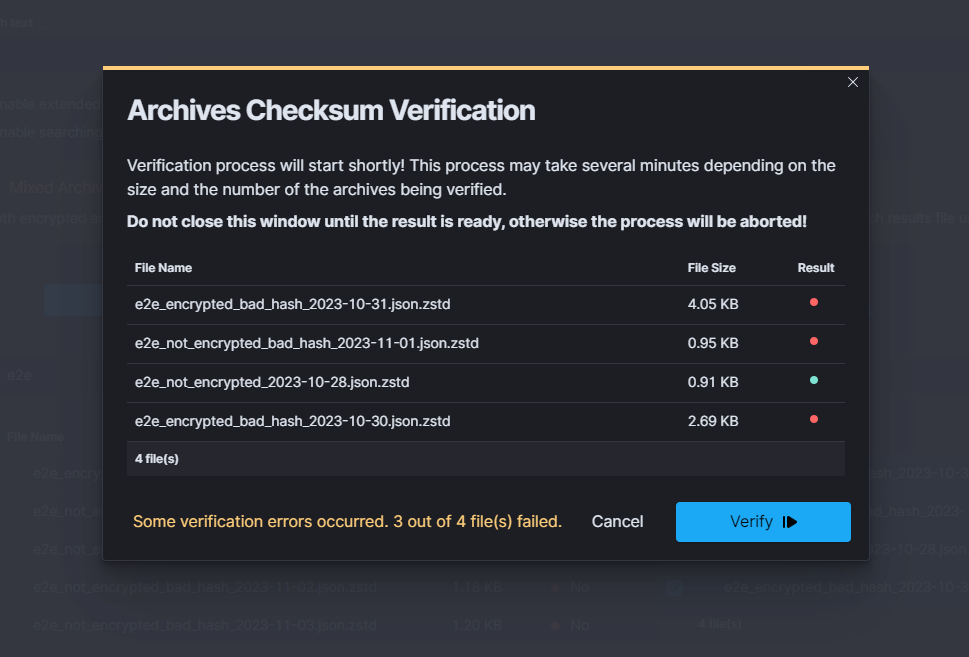
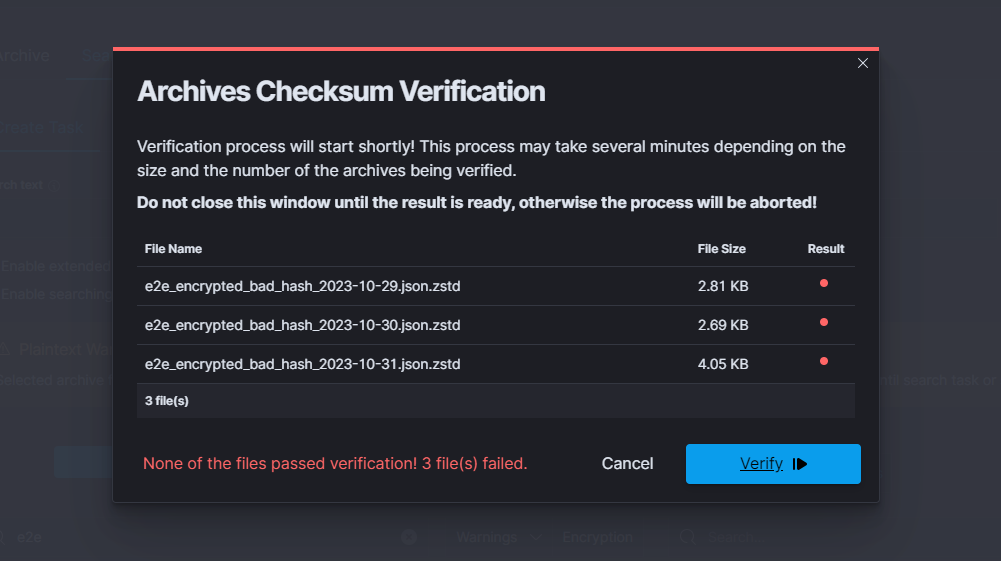
After some time, when the verification is concluded, the final results will be displayed. The verification result is shown in the left bottom corner and is symbolized by one of the displayed colors:
green- all of the archives have compliant checksumsyellow- indicates that some of the archives passed the verification, while others did notred- signifies that all of the selected archives failed the verification process
When all files are okay:
When results are partially correct:
When all files are failed:
As mentioned before, there is an option to hover over the color dot that indicates the verification result of the file. Below picture shows the reason of failed verification of particular file.
Identifying progress of archivisation/restoration process
The /usr/share/logserver-gui/data/archive/tasks directory contains metadata files, that indicates the current status of the task. That files contains informations about all indices, that:
are about to be processed (“Waiting” status)
are processing (“Running” status)
were processed (“Complete” status)
If everything went according to the plan and the process has successfully finished, that metadata file will be removed. However, when some index cannot be processed or something unexpected happened, there will be “Error” status, with detailed message in the “error” field and metadata will remain in the system.
The above described situation is reflected in the GUI by the Status column in the Task List tables.
Moreover, in the metadata files can be found current process id (pid), total documents count and encryption details.
Uncompleted Tasks removal
List archive folder and find filename generated by uncompleted task.
ls -la /archivefolderpath/ -rw-r--r--. 1 user group 13 Mar 21 10:07 prd-srv-win-ad-2022.12. 21_2022-12-21.json.zstd
Find document in
.archiveindex using filename from previous stepcurl -s -k -X GET -ulogserver:... http://127.0.0.1:9200/.archive/_search?size=10000 |jq '.'| grep -B4 "prd-srv-win-ad-2022.12.21"Write down it’s ID
"_id": "Q8teA4cBj_ghAWXFcMJA", "_score": 1.0, "_source": { "date": "2023-03-21T08:52:13.502Z", "filename": "prd-srv-win-ad-2022.12.21_2022-12-21.json.zstd",
Remove documen using saved ID
curl -s -k -X DELETE -ulogserver:... http://127.0.0.1:9200/.archive/_doc/Q8teA4cBj_ghAWXFcMJA
Command Line tools
Archive files can be handled by the following commands zstd, zstdcat, zstdgrep, zstdless, zstdmt.
zstd
The command for decompress *.zstd the Archive files, for example:
zstd -d winlogbeat-2020.10_2020-10-23.json.zstd -o
winlogbeat-2020.10_2020-10-23.json
zstdcat
The command for concatenate *.zstd Archive files and print content on the standard output, for example:
zstdcat winlogbeat-2020.10_2020-10-23.json.zstd
zstdgrep
The command for print lines matching a pattern from *.zstd Archive files, for example:
zstdgrep "optima" winlogbeat-2020.10_2020-10-23.json.zstd
Above example is searching documents contain the “optima” phrase in winlogbeat-2020.10_2020-10-23.json.zstd archive file.
zstdless
The command for viewing Archive * .zstd files, for example:
zstdless winlogbeat-2020.10_2020-10-23.json.zstd
zstdmt
The command for compress and decompress Archive *.zdtd file useing multiple CPU core (default is 1), for example:
zstdmt -d winlogbeat-2020.10_2020-10-23.json.zstd -o winlogbeat-2020.10_2020-10-23.json